Using the Spec Builder Wizard
The Spec Builder is a core feature of the Castlecraft Architect UI. It provides a structured, multi-step wizard to guide you through the process of gathering comprehensive requirements for your software project. This ensures that all necessary details, from high-level goals to specific constraints, are captured before AI-assisted component generation begins.
Overview
The wizard is designed to replace unstructured documents with a standardized, machine-readable format. The data you enter is saved as a Revision Draft and serves as the primary input for the Component Discussion Tool.
You can access the wizard from the main navigation. You can either start a new specification or select an existing draft to continue editing.
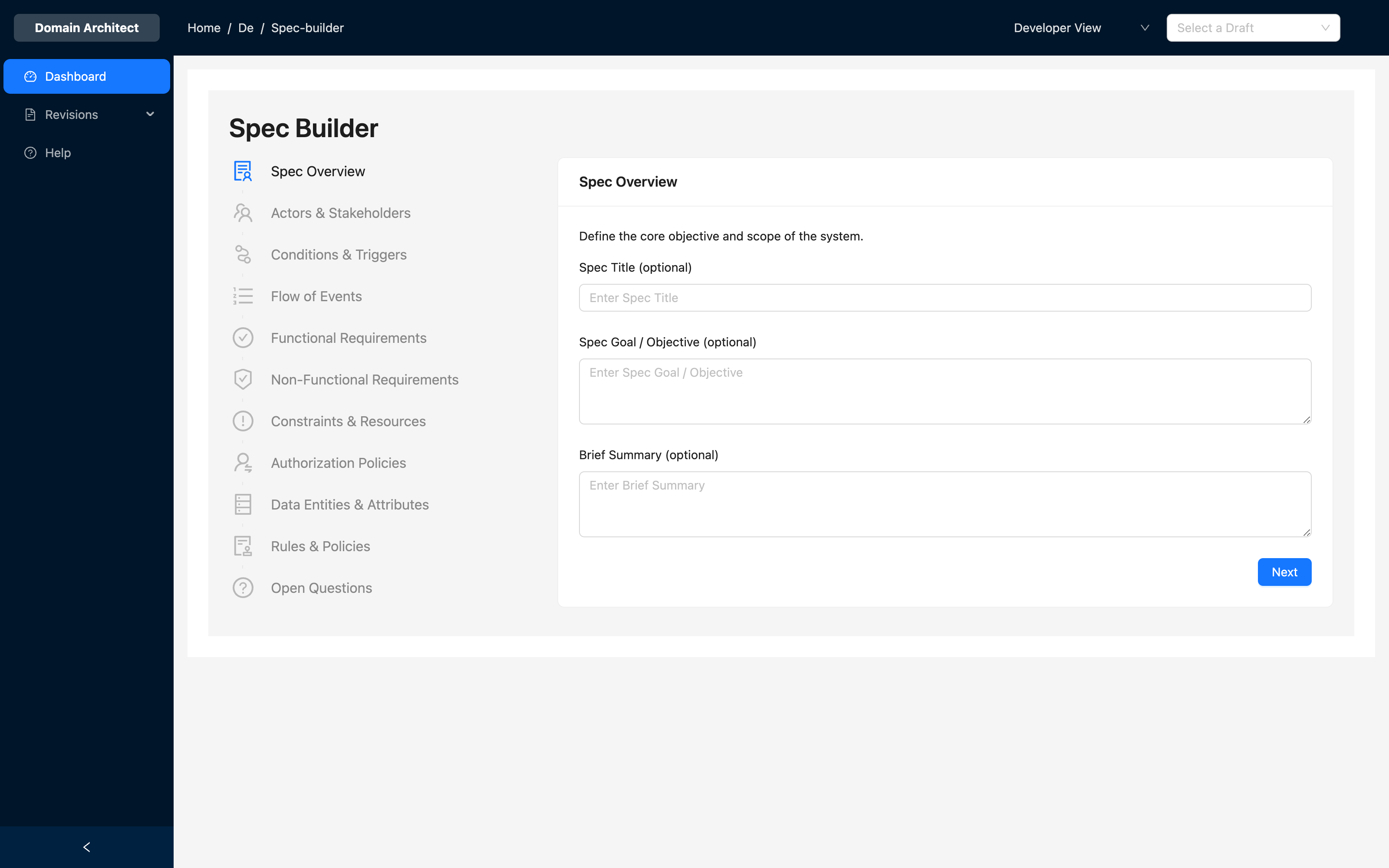
Wizard Steps
The wizard is divided into logical sections to cover all aspects of requirement gathering. Each step corresponds to a critical part of a well-defined software specification.
1. Spec Overview
Define the foundational details of your project.
- Spec Title: A clear, concise title.
- Spec Goal / Objective: What is the primary business goal?
- Brief Summary: An executive summary of the project.
2. Actors & Stakeholders
Identify all the people and roles involved.
- Primary Actors: Users who directly interact with the system.
- Supporting Actors: Systems or users who provide services to the system.
- Stakeholders: Individuals or groups with an interest in the project's outcome.
3. Conditions & Triggers
Define the state of the system before the use case begins and the expected outcomes upon completion.
- Preconditions: What must be true for the use case to start?
- Postconditions (Success): What is the state of the system after a successful run?
- Postconditions (Failure): What is the state of the system if the use case fails?
4. Flow of Events
Describe the step-by-step sequence of interactions between the actors and the system.
- Main Success Scenario: The ideal path where everything goes as planned.
- Alternate Flows: Other success paths or variations from the main flow.
- Exceptional Conditions: How the system should handle errors or exceptional cases.
5. Functional Requirements
List the specific functions and behaviors the system must perform. This is a checklist of what the system does.
6. Non-Functional Requirements (NFRs)
Describe the quality attributes of the system. This is about how the system performs its functions. Examples include performance (e.g., "response time under 200ms"), security, reliability, and usability.
7. Constraints & Resources
Specify any limitations or constraints that the project must operate within.
- Budget Estimate: Financial constraints.
- Timeline: Key deadlines and release dates.
- Team Expertise: Required skills and available resources.
- Technology Constraints: Mandated technologies or platforms (e.g., "must use Node.js").
- Legal or Compliance: Regulatory requirements like GDPR or HIPAA.
8. Authorization Policies
Define the security rules for who can do what.
- Authorization Principles: High-level roles, groups, or attributes used for access control (e.g., "Admin Role", "Document Owner").
- Access Control Rules: Specific rules that connect subjects, actions, and resources (e.g., "Editors can 'edit' 'published' documents").
9. Data Entities & Attributes
Model the key data objects within your domain.
- Data Entities: The main nouns of your system (e.g., "User", "Order", "Product").
- Attributes: The properties of each entity, including their name and data type (e.g., a "User" has a "name" which is a "string").
10. Rules & Policies
List any business rules or organizational policies that the system must enforce.
- Rules: Specific, atomic business logic (e.g., "A premium user can have up to 100 projects").
- Organizational Policies: Broader company-wide policies that impact the system.
11. Open Questions
A place to capture any unresolved issues, assumptions that need validation, or items for future discussion. This ensures that ambiguities are not forgotten.
Discussing with AI
On the final step of the wizard, a "Discuss with AI" button becomes available. This powerful feature opens a chat modal where you can have a conversation with an AI assistant to review and enhance your entire specification.
The AI is provided with the full context of all the data you've entered across every step of the wizard. You can use this to:
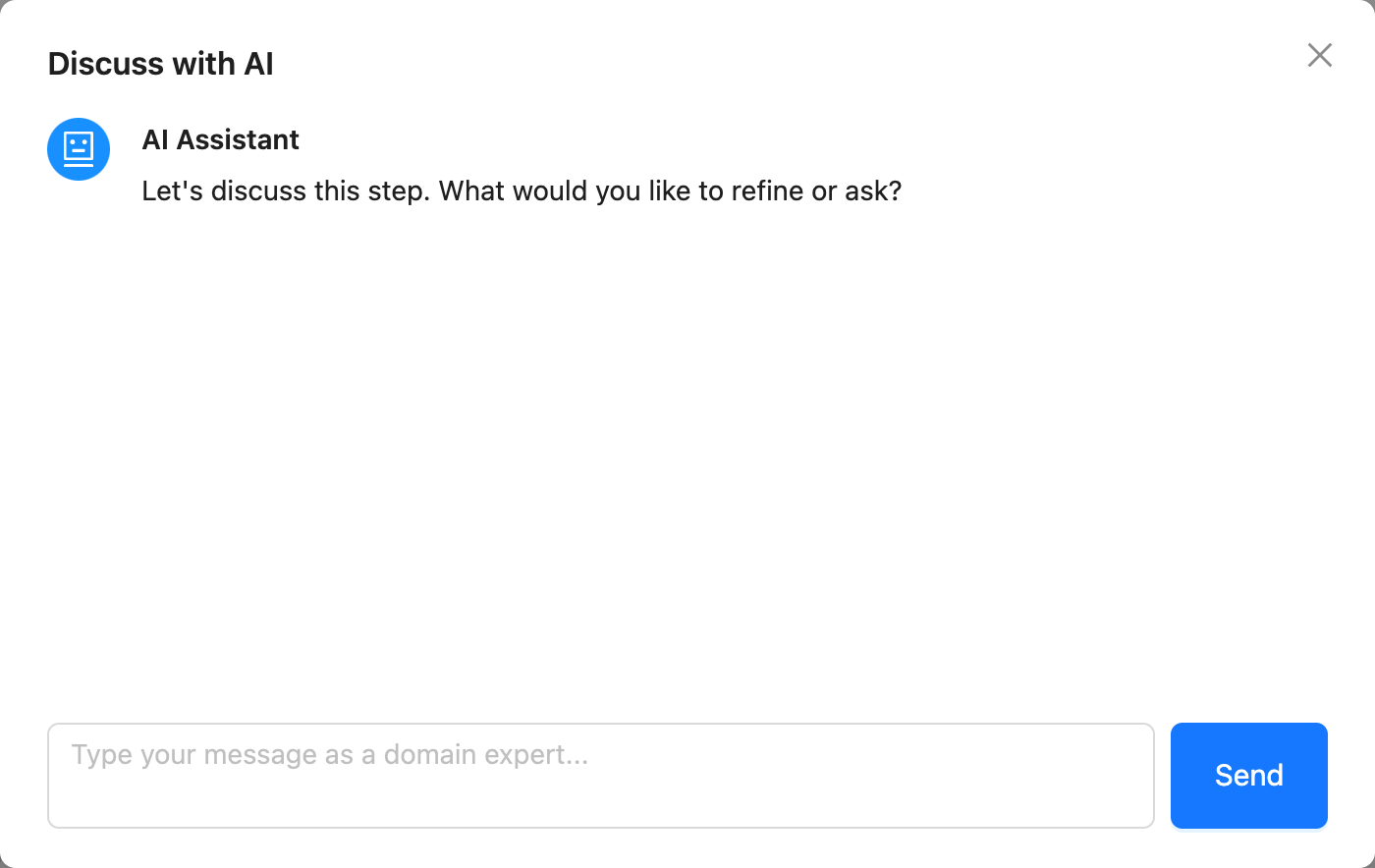
- Ask for a summary of your specification.
- Request improvements to specific sections (e.g., "Flesh out the main success scenario with more detail").
- Brainstorm potential missing requirements (e.g., "What non-functional requirements should I consider for an e-commerce system?").
- Clarify business rules or exceptional flows.
The AI will provide its suggestions and refinements directly in the chat, helping you to create a more robust and complete specification before saving it as a draft.
Saving and Using Your Spec
Once you complete the final step, you have several options available in the bottom-right corner:
- Save as Draft / Update Draft: This will create or update a Revision Draft in the system with all the data you've entered. This is the primary way to persist your work.
- Download: You can export the complete specification data for backup or for sharing with stakeholders. The available formats are:
- JSON: A machine-readable format containing all the raw data.
- PDF: A human-readable document generated directly from the data.
- Markdown PDF: A beautifully formatted PDF generated from a markdown version of your spec, ideal for formal documentation.